Thymosin-Alpha-1 (Research Overview)
Thymosin-Alpha-1 (TA-1) is a 28–amino acid, N-terminally acetylated peptide originally isolated from calf thymus and later synthesized for research and clinical investigation.1,2 It is derived from prothymosin-α and is best characterized as an immune response modulator rather than a direct antimicrobial or cytotoxic agent.
Mechanistic investigations demonstrate that TA-1 influences dendritic cell activation, T-cell maturation, cytokine signaling balance, and innate immune receptor pathways.3-5 Rather than broadly stimulating inflammation, TA-1 enhances immune coordination and antigen responsiveness, particularly in states of immune suppression or dysregulation.3,4
TA-1 (also known internationally as thymalfasin) has been studied clinically for over four decades and has held regulatory approvals in certain countries for chronic hepatitis B and other immune-related indications.⁶
Executive Summary
TA-1 is an endogenous thymic peptide that supports immune signaling efficiency. Primary research demonstrates:
- Enhancement of dendritic cell function and Th1 polarization³
- Modulation of IL-2 receptor expression on T-cells⁵
- Improved antiviral immune responses in chronic hepatitis B trials7,10
- Augmentation of influenza vaccine antibody response in elderly subjects⁸
- Adjunctive immune support in metastatic melanoma randomized trials⁹
TA-1 does not function as a pathogen-directed drug. Its activity centers on immune regulation — particularly the interface between innate sensing and adaptive response.
Key Actions
Dendritic Cell Activation & Th1 Polarization
TA-1 activates dendritic cells and promotes antifungal Th1 resistance via innate signaling pathways.³
IL-2 Receptor Modulation
TA-1 enhances expression of high-affinity IL-2 receptors on human lymphocytes under stimulation conditions.⁵
Innate Immune Signaling Support
TA-1 influences Toll-like receptor–linked pathways that shape adaptive immune priming.3,4
Adjunctive Antiviral Immune Enhancement
Randomized controlled trials in chronic hepatitis B demonstrate improved virologic response rates versus placebo.⁷
Vaccine Response Augmentation
TA-1 enhanced antibody response to influenza vaccination in elderly men in a double-blind placebo-controlled study.⁸
🧬 What Is Thymosin-Alpha-1?
TA-1 was first sequenced and characterized in 1977 as the immunologically active component of thymosin fraction 5.1,2 It consists of 28 amino acids with a molecular weight of approximately 3108 Da.
Unlike monoclonal antibodies or cytokine blockers, TA-1 functions upstream in immune signaling hierarchies. Experimental data indicate it enhances dendritic cell activation and T-cell priming rather than suppressing a single inflammatory mediator.3,4
Core Research Areas
🦠 Chronic Viral Hepatitis (HBV)
The strongest clinical literature for TA-1 comes from chronic hepatitis B. In a randomized controlled trial published in Hepatology, thymosin alpha 1 demonstrated improved complete response rates compared with placebo in HBeAg-positive patients.⁷ A subsequent multicenter phase III randomized trial published in Journal of Viral Hepatitis reported immunologic and virologic response improvements in selected patient populations.10
These studies positioned TA-1 as an immune-modulating adjunct rather than a direct antiviral compound.
💉 Vaccine Response in Older Adults
In a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study, elderly male subjects receiving TA-1 alongside influenza vaccination demonstrated enhanced antibody responses compared to placebo.⁸ This remains one of the clearest demonstrations of TA-1’s immune “response-shaping” capability in humans.
🧬 Dendritic Cell Biology
Romani et al. demonstrated that TA-1 activates dendritic cells and promotes antifungal Th1 resistance through innate immune pathways.3 This work established TA-1 as a bridge between innate immune sensing and adaptive Th1 polarization.
🧫 Oncology Adjunctive Immunotherapy
In a large randomized study of metastatic melanoma, thymosin alpha 1 was evaluated in combination with dacarbazine and interferon alfa.9 While not a cytotoxic therapy itself, TA-1 showed immune-supportive effects in combination regimens, supporting further evaluation in adjunctive oncology settings.
⏳ Immune Aging & Thymic Involution
Age-associated thymic involution reduces naïve T-cell output and immune adaptability.11 TA-1 has been studied as a strategy to enhance immune responsiveness in aging populations, particularly in the vaccine context.8,11
🧪 Mechanistic Insights
- Enhances dendritic cell maturation³
- Promotes Th1 cytokine polarization³
- Modulates IL-2 receptor expression⁵
- Influences innate receptor signaling pathways⁴
TA-1 improves immune coordination without provoking uncontrolled inflammatory amplification.
Molecular Details
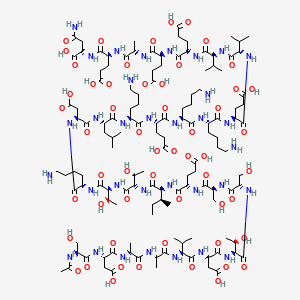
Sequence:
Ac-Ser-Asp-Ala-Ala-Val-Asp-Thr-Ser-Ser-Glu-Ile-Thr-Thr-Lys-Asp-Leu-Lys-Glu-Lys-Lys-Glu-Val-Val-Glu-Glu-Ala-Glu-Asn
Molecular Formula: C₁₂₉H₂₁₅N₃₃O₅₅
Molecular Weight: 3108.3 Da
CAS Number: 62304-98-7
References:
- Goldstein AL, Low TL, McAdoo M, et al. Thymosin alpha1: isolation and sequence analysis of an immunologically active thymic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977;74(2):725-729. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.2.725
- Low TL, Thurman GB, McAdoo M, et al. The chemistry and biology of thymosin. I. Isolation, characterization, and biological activities of thymosin alpha1. J Biol Chem. 1979;254(3):981-986.
- Romani L, Bistoni F, Perruccio K, et al. Thymosin alpha1 activates dendritic cells for antifungal Th1 resistance. Blood. 2004;103(11):4232-4239. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-08-2922
- King R, Tuthill C. Immune modulation with thymosin alpha 1 treatment. Vitam Horm. 2016;102:151-178. doi:10.1016/bs.vh.2016.04.003
- Leichtling KD, Serrate SA, Sztein MB. Thymosin alpha 1 modulates the expression of high affinity interleukin-2 receptors on normal human lymphocytes. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1990;12(1):19-29. doi:10.1016/0192-0561(90)90064-T
- Billich A. Thymosin alpha1. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2002;3(5):698-707.
- Chien RN, Liaw YF, Chen TC, et al. Efficacy of thymosin alpha1 in patients with chronic hepatitis B: a randomized, controlled trial. Hepatology. 1998;27(5):1383-1387. doi:10.1002/hep.510270527
- Gravenstein S, Duthie EH Jr, Miller BA, et al. Augmentation of influenza antibody response in elderly men by thymosin alpha one. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1989;37(1):1-8.
- Maio M, Mackiewicz A, Testori A, et al. Large randomized study of thymosin alpha 1, interferon alfa, or both in combination with dacarbazine in metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(10):1780-1787. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.5208
- Mutchnick MG, Lindsay KL, Schiff ER, et al. Thymosin alpha1 treatment of chronic hepatitis B: results of a phase III multicentre randomized study. J Viral Hepat. 1999;6(5):397-403.
- Aspinall R, Lang PO. Interventions to restore thymic function in aging. Immunol Today. 2002;23(7):343-348.